Designing Big Data - Charter Communications
Designed useful tools, product workflows and features to curate, represent, visualize all the performance & customer feedback data for all charter’s products & services across cable, internet and digital apps.
Skills
UX - UIUser ResearchStrategic DesignDesign ManagementPrototypingToolkit
Research TechniquesFigmaCharter Design Lib (KITE)Impact
PrismVoice of CustomerTech MobileHiveDuration
9 months 
Project Overview
Background
Charter Communications, Inc. is an American telecommunications and mass media company with services branded as Spectrum. With over 57 million customers in 41 states, it is the largest cable operator in the United States by subscribers.
It caters to the unique needs of small and medium-sized businesses with a collection of cost-effective connectivity products that includes Internet, business telephone, Mobile and Video services. Spectrum’s connectivity products – Spectrum Internet, Mobile, streaming and linear Video, and Voice – seamlessly converge to power the customers' digital lives.
Working for the Data Insights team, I was responsible for Enterprise data tools such as Prism, Voice of Customer, Techmobile and Hive which collect, maintain and represent all the product and services performance data and overall customer experience data for the company across cable, internet and digital app services.
Task as. Designer
-

Insightful design from complex data
-

Improved UX
-

Contribute to Brand Value
Voice of Customer
Voice of Customer (VOC) serves as a centralized hub for all customer experience data—including feedback, reviews, reported issues, service outages, and other experience-related insights—providing a unified view of user sentiment and behavior across all touchpoints.
Technical Overview
The Voice of Customer (VOC) at Charter serves as a centralized data warehouse and analytical hub for all customer experience-related data. It aggregates and stores structured and unstructured feedback from multiple touchpoints, including customer reviews, survey responses, support interactions, app and web feedback, error logs, service outages, and behavioral experience signals.
VOC acts as the authoritative endpoint for accessing and analyzing this comprehensive dataset. Charter employees—from product managers to customer experience teams—leverage VOC to gain actionable insights into customer sentiments, pain points, and systemic issues. The system enables users to filter, categorize, and drill down into feedback using a robust information architecture and tagging framework.
Data within VOC is normalized and organized into a taxonomy of categories and subcategories. These classifications are often powered by both rule-based logic (keyword matching) and machine learning models for natural language processing (NLP), which help identify themes, trends, and root causes at scale.
This centralized architecture supports cross-functional investigations, enables performance monitoring of Charter's products and services, and informs strategic decisions by providing a clear and unified view of the customer experience across the organization.
VOC - Projects 1
Categorize Review Redesign
At Charter, customer reviews are collected from various channels—including the website, mobile app, and customer service—and need to be systematically organized. These reviews are grouped into main categories, which are further broken down into subcategories, creating a tree-like parent-child structure. Each category is associated with a set of keywords that users can select to tag the review. Based on the selected keyword, a dynamic dropdown reveals relevant subcategories for more precise classification.
I led the UX - UI design, Information architecture, and Interaction design for this B2B tool for categorization system—ensuring a seamless and intuitive parent-child workflow that supports consistent and scalable review organization across all channels by the VOC team at Charter.
Defining group to classify Customer reviews
-
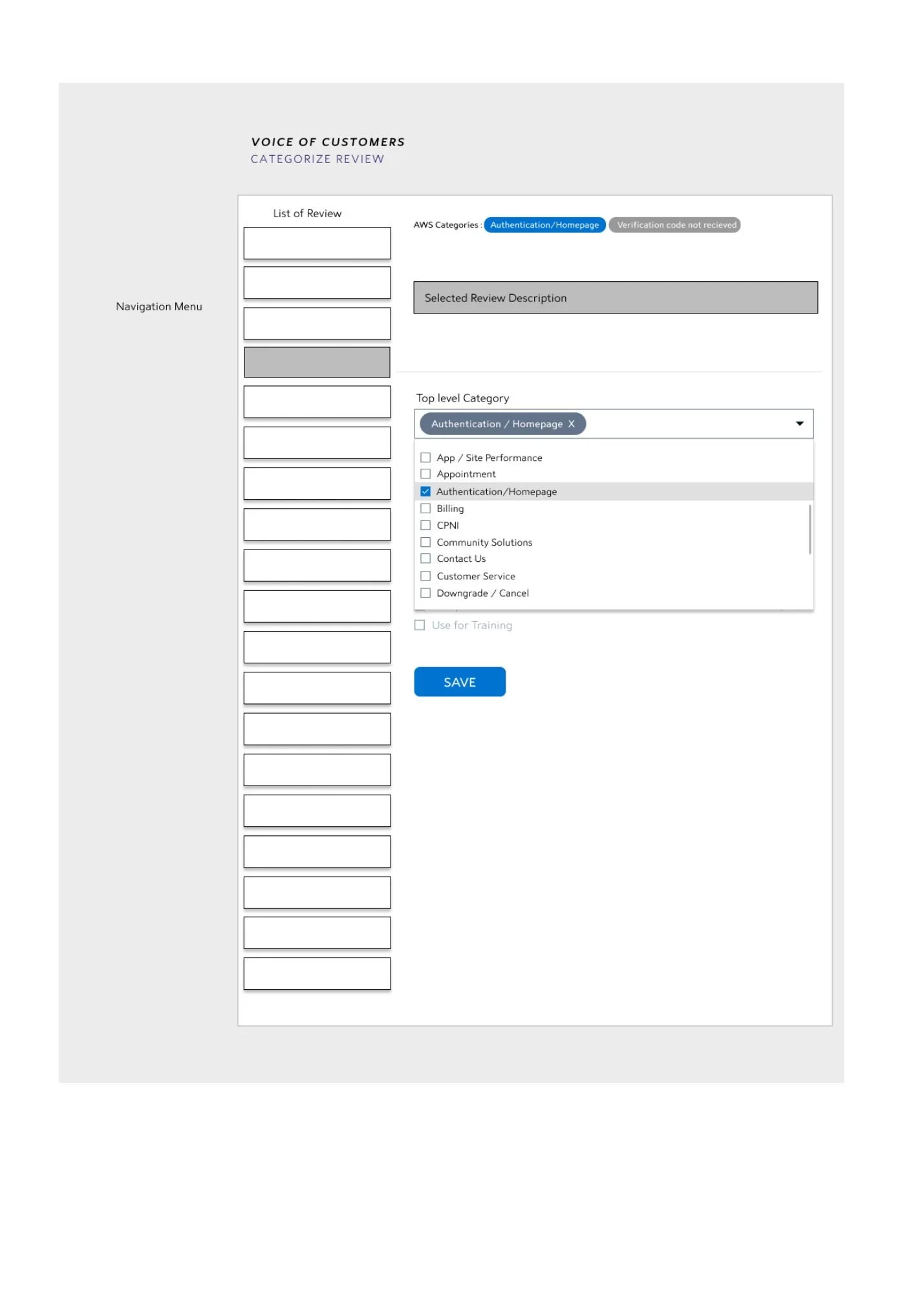
Top Level category
These are Parent type of category that are also called applied category. These are the broader level of classification in terms of segregation.
Eg: Customer service, Billing etc.
-
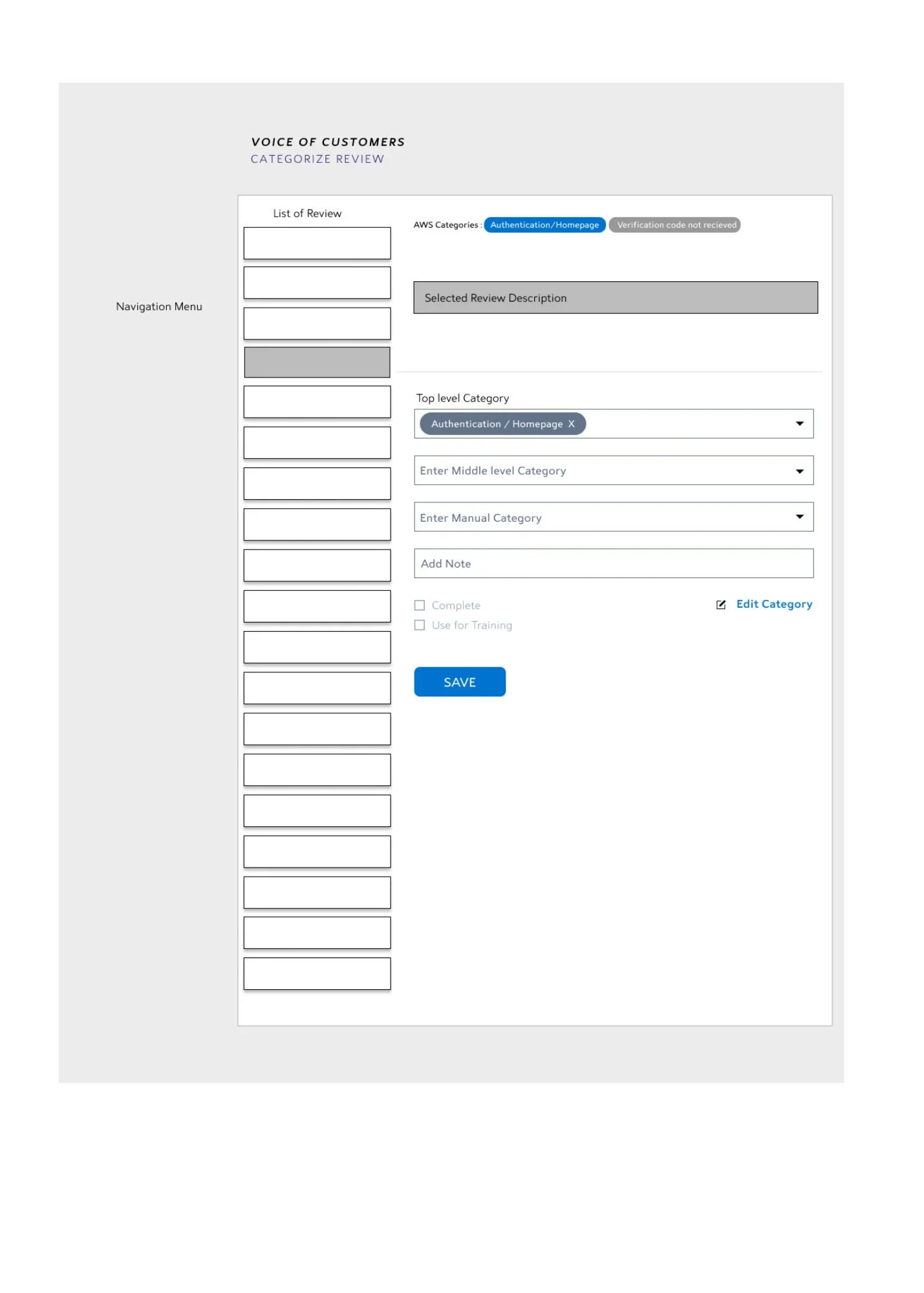
Middle Level category
These are Child type of category that are also called applied sub category. These are the sub level of classification of top level applied categories.
Eg: Customer service > Unable to Login
Billing > Unable to make payments
-
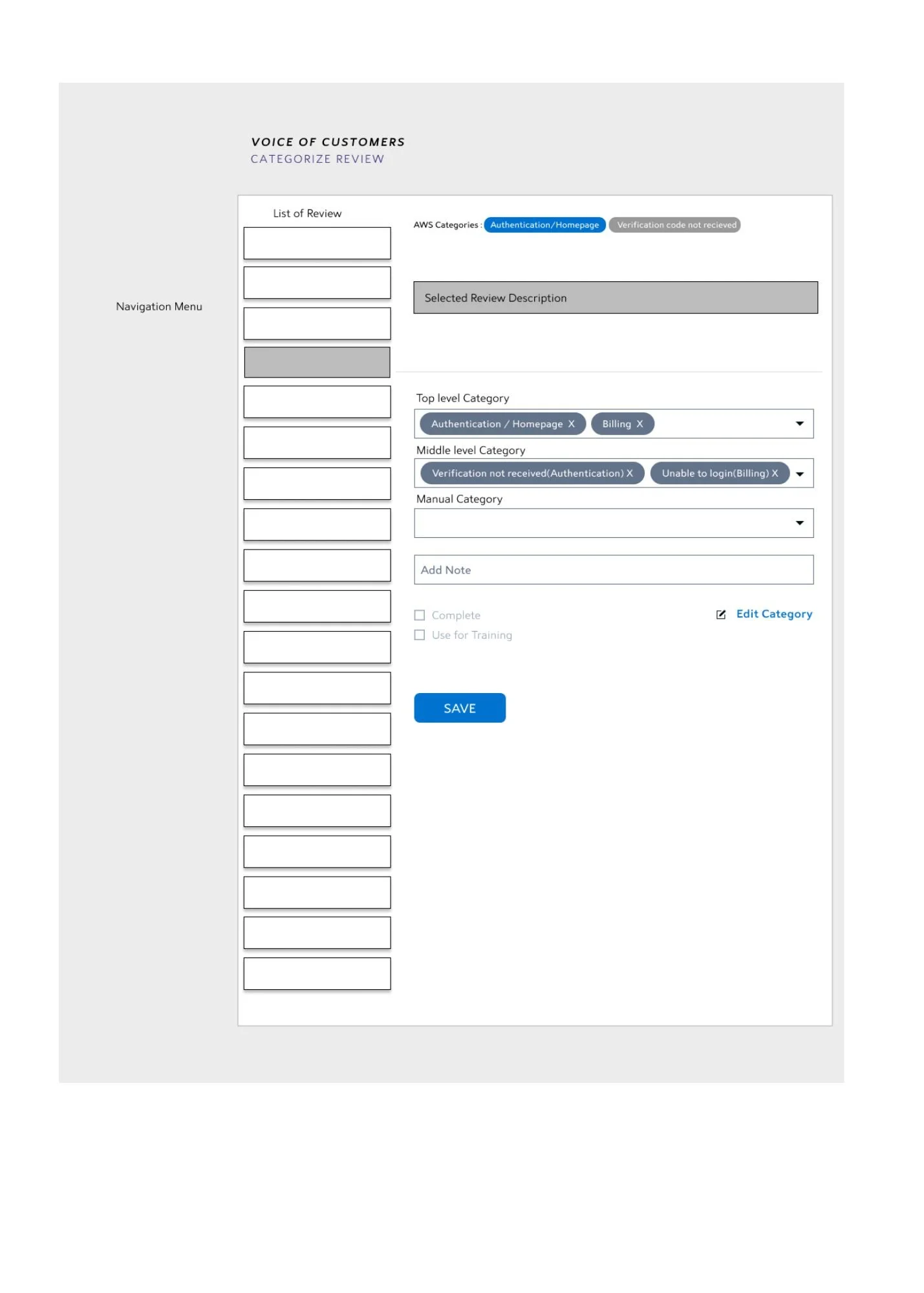
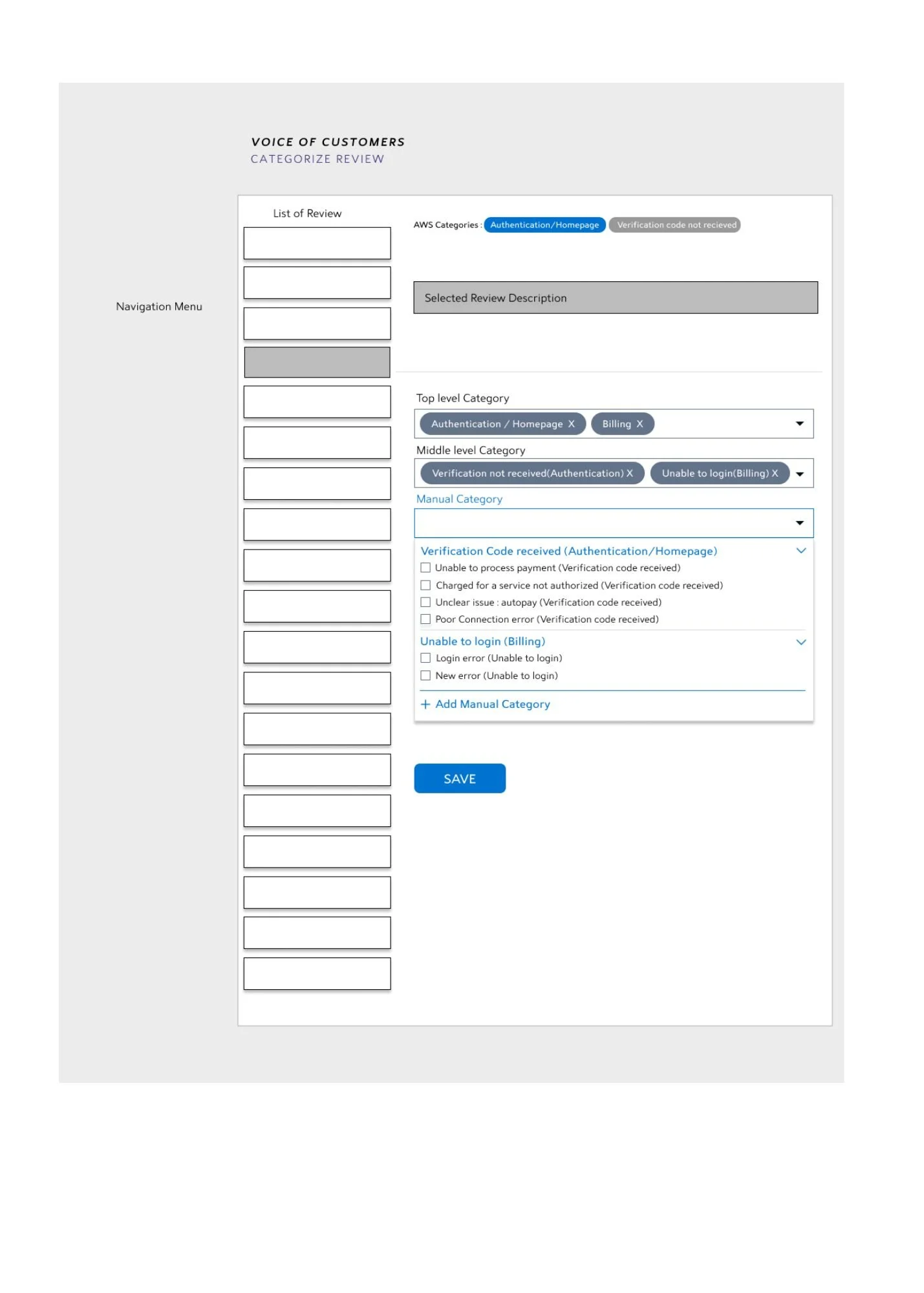
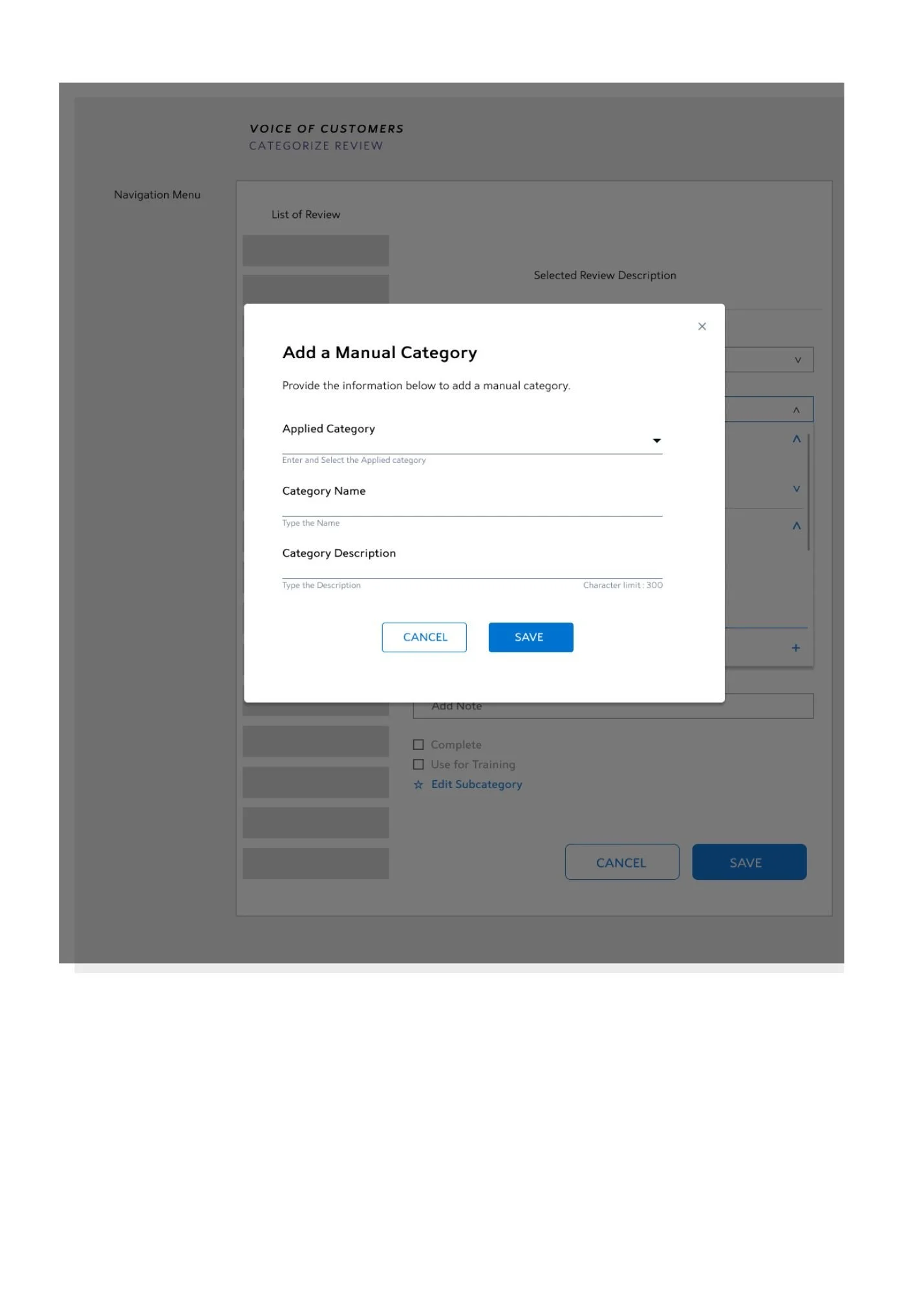
Manual Category
These are categories which are manually defined by the user. Sometimes the feedback need to be put in a specific use case. Other times there are no broader bag in which a special case can be booked. Hence these are also called as custom categories which hold more specific usecases.
Eg: Billing > Unable to make payment > payment gateway is corrupt.
Wireframes for Categorize Review
Wireframes for Scenarios regarding Add | Edit | Delete a Category
Realtime Designs
-

Categorize reveiw in VOC within Prism
The image shows a scenario inside Prism > Voice of customer > Categorize Review Tab. A list of reviews on the left-hand side are populated, and on the right-hand side the user can categorize the review.
The form with category textboxes is filled with suitable feilds and below you can find a link to edit manual categories.
-

Selecting appropriate category type
A single review can be assigned to two different categories, and hence the subcategory dropdown will be populated with the respective subcategory lists. One can also add a manual category at any time through the floating bottom button at the end of the dropdown.
VOC - Projects 2
Redesign Filter Menu
Another interesting way of approaching this question was by interviewing sales team and client support team who interact with customers on everyday basis and understand client needs based on their experiences. They also provided us with examples of anecdotes from their interactions with customers, this gave us numerous insights on customer mindset, decision making anxiety, wish list while they select or purchase our recruitment services. We also collected their thoughts about what according to them, a better, simpler experience would look like for the customers.
Another important aspect to keep in mind is the original structure of your product and keeping product managers and engineers in the fold. They know the structure of the product and how its build in a ‘bit by bit’ process based on the evolving needs of the business and clients along the way.
What was the problem with old filter menu?
Advanced Filters in VOC are a set of metadata-based criteria—such as source, environment, and contextual attributes—used to segment customer reviews. Accessed via a click-to-open panel from the right, the legacy filter menu presented several usability issues. It used a fixed rectangular layout where the number of criteria exceeded the visible area, forcing users to scroll extensively to reach lower options (refer to image for legacy design).
Key limitations included:
Lack of hierarchy: Fields were added incrementally over time with no logical grouping, resulting in a disorganized layout.
Limited input flexibility: Most filters were binary, offering minimal control over value selection.
Disruptive layout behavior: The menu overlaid the categorization form, obscuring core page content and interrupting user workflow. These issues significantly impacted usability and efficiency, prompting a full redesign of the advanced filter experience.
Feature in New Design
The VOC product and engineering teams initiated a complete redesign of the filter menu, aiming to overhaul both its UI and UX for improved efficiency and usability. Multiple design concepts were proposed to streamline the user experience and optimize performance. Following stakeholder discussions and impact analysis, select high-impact features were prioritized for implementation. The enhanced Advanced Filter Menu includes the following key functionalities:
Field Search Bar – Prioritizes frequently used fields for quick access
Field Grouping – Logical grouping of related fields for better navigation
Custom Views – User-defined configurations for tailored filtering
Saved Views – Ability to save and reuse filter configurations
Elastic Search Fields – Real-time, flexible search across filter parameters